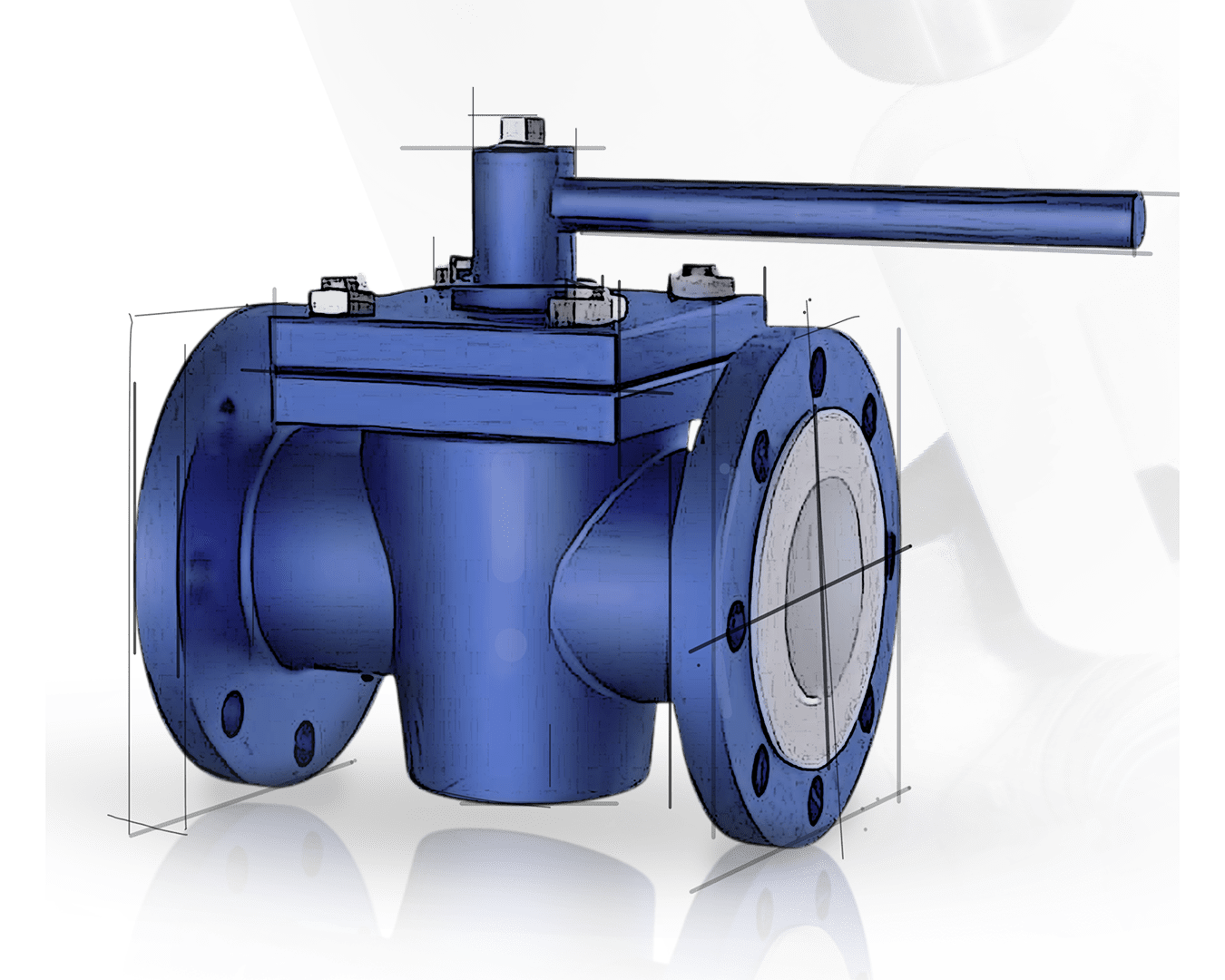
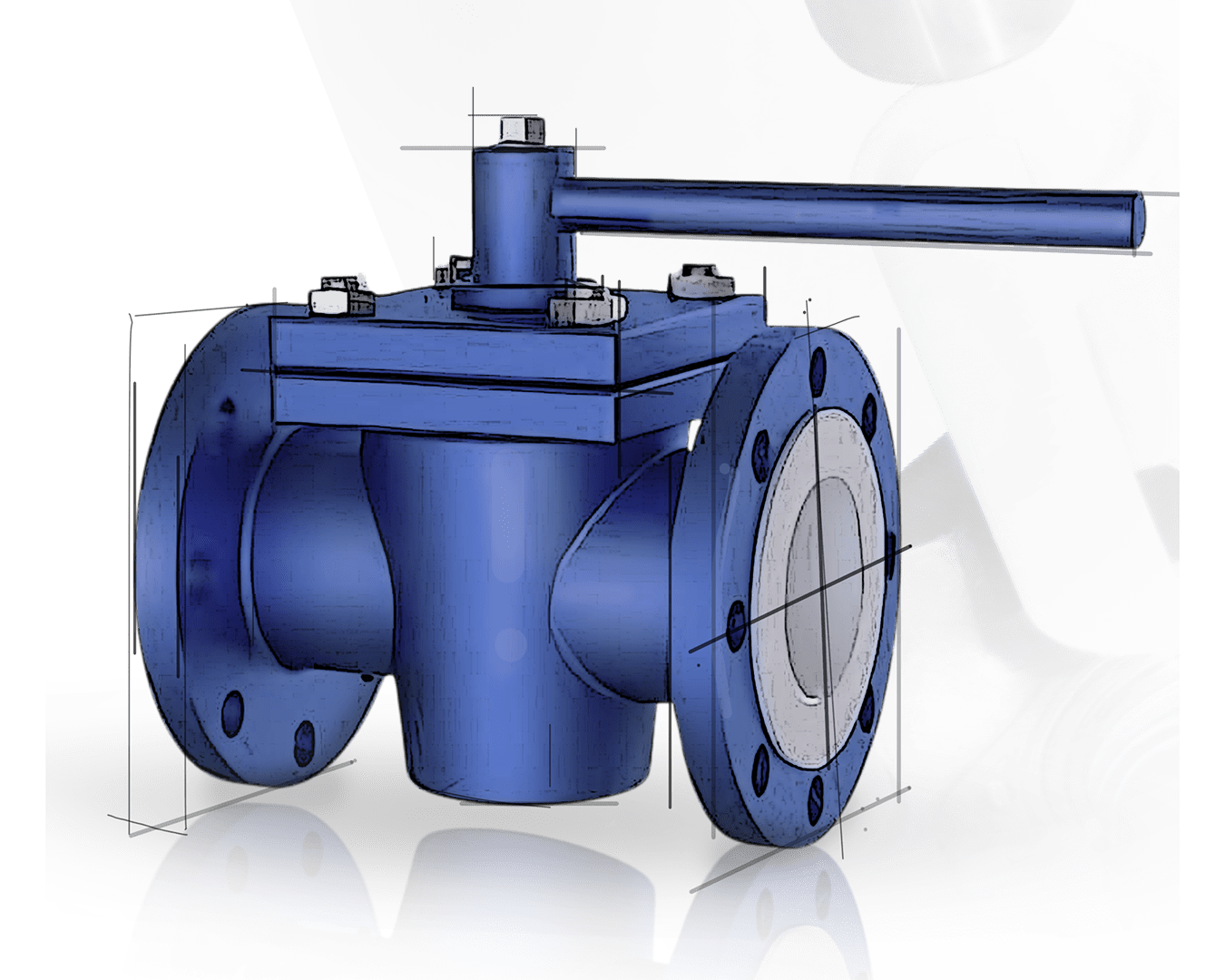
A Lubricated Plug Valve is a quarter-turn valve that uses a sealing lubricant to reduce friction and provide a tight shutoff. It is ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications in industries such as oil & gas, petrochemicals, and power plants
Lubricated Plug Valve
A Lubricated Plug Valve is a quarter-turn valve designed for on-off and throttling applications. It features a cylindrical or tapered plug with a central passage that aligns with the flow path when open. The valve is lubricated with a special sealant to reduce friction and ensure a tight shutoff, making it ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. These valves are widely used in industries requiring reliable performance, minimal leakage, and smooth operation under demanding conditions.
Types of Lubricated Plug Valve
- Regular Pattern Plug Valve – Offers full flow with minimal resistance, suitable for general industrial applications.
- Short Pattern Plug Valve – Compact design for limited space installations.
- Tapered Plug Valve – Features a tapered plug for tight sealing and enhanced durability.
- Pressure Balanced Plug Valve – Designed to handle high-pressure applications while reducing operational torque.
- Jacketed Plug Valve – Includes a heating jacket to maintain media temperature in applications like molten sulfur and asphalt.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
✔ Leak-Proof Sealing – Lubrication fills micro-clearances, ensuring bubble-tight shutoff.
✔ High-Pressure Handling – Suitable for applications up to Class 2500 pressure rating.
✔ Smooth Operation – Lubrication reduces friction, preventing wear and prolonging service life.
✔ Corrosion Resistance – Lubricant acts as a protective layer against corrosive media.
✔ Versatile Applications – Used in oil & gas, petrochemical, water treatment, and power plants.
Disadvantages
✖ Regular Maintenance Required – Periodic lubrication is necessary for optimal performance.
✖ Higher Initial Cost – More expensive than non-lubricated plug valves due to additional sealing features.
✖ Potential Sealant Contamination – Some applications require specific, non-contaminating lubricants.
Specifications | Features |
|---|---|
Type : Lubricated Plug Valve End Connection: Flanged, Threaded (BSP/NPT), Socket Weld, Butt Weld Size: ½” to 24” Pressure Rating: ANSI Class 150, 300, 600, 900, 1500, 2500 Temperature Range: -50°C to 400°C MOC (Material of Construction): Carbon Steel (WCB, LCB), Stainless Steel (CF8, CF8M, CF3, CF3M), Alloy Steel, Duplex, Super Duplex, Hastelloy, Monel Design Standard: API 6D, API 599, ASME B16.34, BS 5353 Cycle Life: High cycle life for industrial applications Face to Face: As per ASME B16.10 and API 6D Operation: Manual (Lever/Gear), Pneumatic Actuator, Electric Actuator, Hydraulic Actuator Fire Safe Design: API 607 / API 6FA compliant Testing: Hydrostatic and Pneumatic Testing as per API 598 / API 6D Documents: Material Test Certificate (MTC), Pressure Test Report, Fire Safe Test Report, PMI Report, IBR & Third-Party Inspection Certificate |
|
Related Products
FAQ’s
Have a question before you buy our products? Take a look at the FAQs below.
If you don’t find the answer you’re looking for, get in touch with us here.
- What is a Lubricated Plug Valve?
- How does a these Plug Valve work?
The valve operates by rotating a cylindrical or tapered plug inside the valve body. The plug has a passage that aligns with the pipeline when open, allowing flow. A special sealant is injected between the plug and the body to enhance sealing and reduce wear.
- What are the advantages of these Plug Valve?
- Leak-proof sealing due to the injected lubricant
- Low friction operation for smooth movement
- High pressure and temperature resistance
- Longer service life compared to non-lubricated valves
- Suitable for throttling and shut-off applications
- What are the disadvantages of a these Valve?
- Requires regular lubrication maintenance
- Higher initial cost than non-lubricated plug valves
- Lubricant may require compatibility checks for specific media
- What industries use these Valves?
These valves are commonly used in oil & gas, petrochemicals, water treatment, power plants, mining, and chemical processing due to their durability and tight sealing properties.
- What materials are used in these Valves?
Common materials include carbon steel (WCB, LCB), stainless steel (CF8, CF8M), duplex steel, Hastelloy, Monel, and Inconel, depending on the application requirements.
- What is the pressure and temperature range of a Lubricated Plug Valve?
Lubricated plug valves can handle pressures up to Class 2500 and temperatures ranging from -50°C to 400°C, depending on the material and design.
- How often does a Lubricated Plug Valve need maintenance?
Regular lubrication is required based on the operating conditions. For critical applications, scheduled lubrication ensures optimal performance and extended valve life.
- Can these Valve be automated?
Yes, these valves can be fitted with pneumatic, electric, or hydraulic actuators for remote operation and automation in industrial settings.
- How is a Lubricated Plug Valve tested?
Testing is performed as per API 598 and API 6D standards, including hydrostatic, pneumatic, and fire-safe testing to ensure leak-proof performance and durability.
Industries where Lubricated Plug Valve is Used
Oil & Gas Refineries
Petro Chemicals
Power Generation
Water Treatment
Pharmaceutical Industry
Application
- Oil & Gas Industry – Used in upstream, midstream, and downstream processes.
- Petrochemical Plants – Handles hydrocarbons, chemicals, and aggressive fluids.
- Power Plants – Used in steam, cooling, and fuel handling systems.
- Water Treatment Plants – Controls potable water, wastewater, and slurries.
- Pharmaceutical Industry – Ensures contamination-free and hygienic fluid control.
- Mining and Slurry Handling – Suitable for abrasive media and high-pressure environments.